List Of Electronegativity Chart With Values
Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons. It is defined as the power of an atom in a compound to attract electrons to itself. In general, atoms with a higher electronegativity value tend to attract electrons more strongly than atoms with a lower electronegativity value.
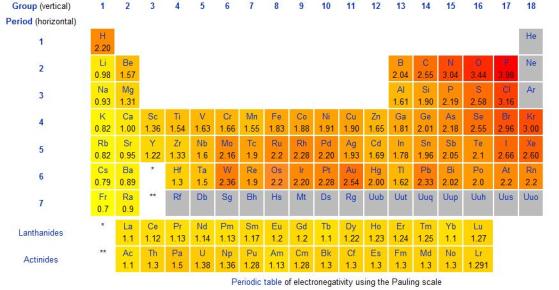
Here is a table of the electronegativities of the elements:
| Element | Electronegativity |
|---|---|
| Fluorine | 4.0 |
| Oxygen | 3.5 |
| Nitrogen | 3.0 |
| Chlorine | 3.0 |
| Carbon | 2.5 |
| Bromine | 2.8 |
| Iodine | 2.5 |
| Hydrogen | 2.2 |
| Sodium | 0.9 |
| Potassium | 0.8 |
| Calcium | 1.0 |
| Magnesium | 1.2 |
| Aluminum | 1.5 |
| Silicon | 1.8 |
| Phosphorus | 2.1 |
| Sulfur | 2.5 |
| Chlorine | 3.0 |
| Argon | - |
| Neon | - |
Note that the electronegativity values of some elements, such as neon and argon, are not well-defined because these elements do not form compounds with other elements. Additionally, electronegativities can vary depending on the specific compound and the environment in which it is measured.







Comments
Post a Comment