Understanding Break-Even Analysis
A break-even analysis is a pivotal financial tool used by businesses to pinpoint the moment at which they transition from operating at a loss to generating profits. This analysis hinges on the delicate balance between fixed costs, variable costs, and the selling price of products or services.
Fixed Costs: The Invariable Expenditures
Fixed costs represent the expenditures that remain impervious to shifts in production or sales levels. They encompass items such as rent, salaries, insurance, depreciation, and other overhead expenses.
Variable Costs: Expenses in Flux
Variable costs, on the other hand, are expenses that fluctuate in direct response to changes in production or sales volumes. These costs include items like materials, direct labor, and other expenses intricately linked to the production of goods or the delivery of services.
The Contribution Margin: The Profitability Indicator
The contribution margin serves as a critical indicator, denoting the distinction between the selling price of a unit and the variable cost per unit. This margin assumes a central role as it signifies the amount each unit contributes toward covering fixed costs and generating a profit.
Formula for Contribution Margin:
Contribution Margin = (Sales Price per Unit) - (Variable Cost per Unit)
Calculating the Break-Even Point in Units
To ascertain the break-even point in terms of units, one must divide fixed costs by the contribution margin per unit. This calculation reveals the number of units that must be sold to cover fixed costs and achieve the break-even point.
Formula for Break-even Analysis in Units:
Break-even Analysis in Units = Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin per Unit
Determining the Break-Even Point in Sales Revenue
For those looking to gauge the break-even point in terms of sales revenue, this calculation can be achieved by multiplying the sales price per unit by the number of units required to break even. This provides the total sales revenue necessary to cover fixed costs.
Formula for Break-even Analysis in Sales ($):
Break-even Analysis in Sales ($) = Sales Price per Unit × Break-even Analysis in Units
Applying Break-Even Analysis
A break-even analysis can be applied to specific products, services, or the entirety of a business. It offers valuable insights into financial health and sustainability. Once the break-even point has been ascertained, a clear understanding emerges regarding the number of units or sales revenue required to attain profitability.
The Dynamic Nature of Break-Even Analysis
It is crucial to bear in mind that a break-even analysis is a dynamic tool that equips businesses to make informed decisions regarding pricing, cost management, and business expansion. Regularly revisiting and updating the analysis is of paramount importance, especially when changes occur in fixed costs, variable costs, or pricing strategies. This ongoing process ensures that a business remains on the path to profitability.
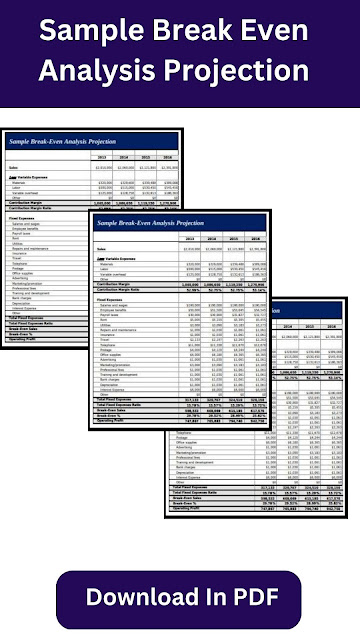
Break Even Analysis Template
Download Here
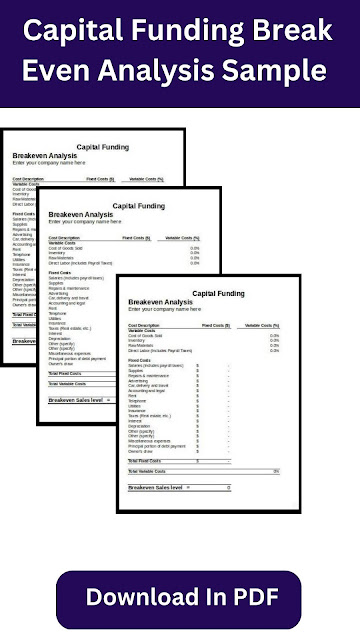
Break Even Point Analysis
Download Here
How to Create a Break-Even Analysis
Creating a break-even analysis involves a few key steps, which are outlined below:
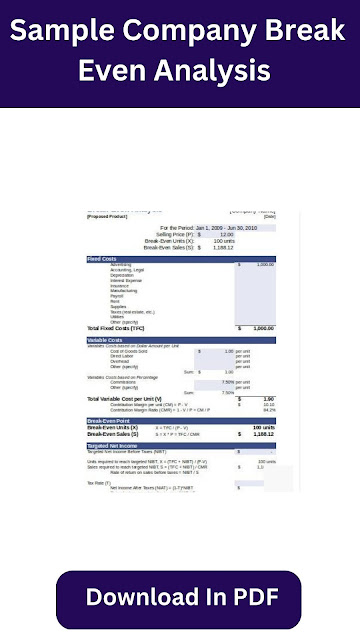
Determine the Fixed Costs: Fixed costs are those costs that remain the same regardless of the volume of sales. These costs may include rent, salaries, insurance, and utilities. You should gather all relevant fixed costs and add them up.
Download Here
Identify the Variable Costs: Variable costs are costs that change with the volume of sales. These costs may include raw materials, labor, and shipping costs. You should identify all relevant variable costs and calculate the total variable cost per unit.
Determine the Break-Even Point: The break-even point is the number of units the business needs to sell to cover its total costs. You can calculate this by dividing the total fixed costs by the contribution margin. This will give you the number of units you need to sell to break even.
Helps determine the minimum sales required: A break-even analysis helps businesses determine the minimum number of products or services they need to sell to cover their costs. This information can be useful in setting sales targets and pricing strategies.
Helps assess profitability: Break-even analysis can help businesses determine how much they need to sell in order to make a profit. By analyzing the relationship between sales volume and costs, businesses can identify the point where their revenues will exceed their expenses.
What are the benefits of performing a break-even analysis
Performing a break-even analysis can provide a number of benefits for businesses, including:
Helps in decision-making: A break-even analysis provides a clear understanding of the costs involved in a business and the impact of different pricing or cost-cutting strategies. This information can help in making informed decisions about production, marketing, and pricing strategies.
Helps to identify risks: By analyzing the break-even point, businesses can identify the risks associated with sales or revenue shortfalls. This can help in planning and preparing for potential downturns in sales.
Helps in setting prices: By understanding the costs involved in producing a product or providing a service, businesses can set prices that will help them remain competitive while still covering their costs.
Helps in financial planning: A break-even analysis can help businesses forecast future revenues and expenses, which can help in financial planning and budgeting.
In summary, a break-even analysis can be an essential tool for businesses to understand their financial health, assess profitability, and make informed decisions.







Comments
Post a Comment